Urinary incontinence is leaking of urine that you can't control. While
it may not be dinner-table conversation, many American men and women suffer
from urinary incontinence. We don't know for sure exactly how many.
That's because many people do not tell anyone about their symptoms.
They may be embarrassed, or they may think nothing can be done. So they
suffer in silence.
Urinary incontinence is not a disease. It is a symptom of many conditions.
Causes may differ for men and women. But it is not hereditary. And it
is not just a normal part of aging. It can affect emotional, psychological
and social life. Many people who have urinary incontinence are afraid
to do normal daily activities. They don't want to be too far from
a toilet. Urinary incontinence can keep people from enjoying life.
Many people think urinary incontinence is just part of getting older. But
it's not. And it can be managed or treated.
A quarter to a third of men and women in the United States suffer from
urinary incontinence. That means millions of Americans. About 33 million
have overactive bladder (also known as OAB) representing symptoms of urgency,
frequency and with or without urge incontinence.
Studies show that many things increase risk. For example, aging is linked
to urinary incontinence. Pregnancy, delivery, and number of children increase
the risk in women. Women who have had a baby have higher rates of urinary
incontinence. The risk increases with the number of children. This is
true for cesarean section (C-section) and vaginal delivery.
Women who develop urinary incontinence while pregnant are more likely to
have it afterward. Women after menopause (whose periods have stopped)
may develop urinary incontinence. This may be due to the drop in estrogen
(the female sex hormone). Taking estrogen, however, has not been shown
to help urinary incontinence.
Men who have prostate problems are also at increased risk. Some medications
are linked to urinary incontinence and some medicines make it worse. Statistics
show that poor overall health also increases risk. Diabetes, stroke, high
blood pressure and smoking are also linked.
Obesity increases the risk of urinary incontinence. Losing weight can improve
bladder function and lessen urinary incontinence symptoms.
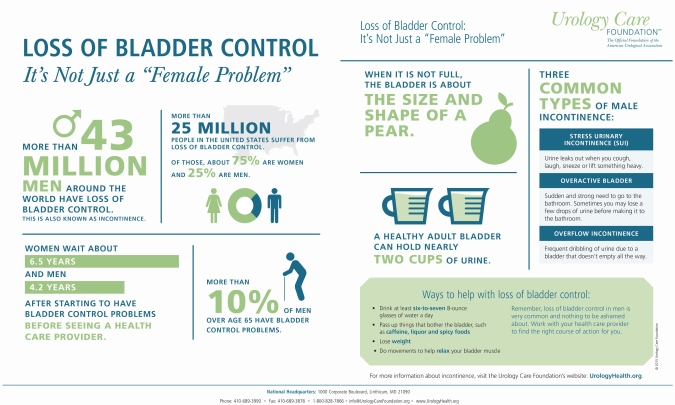
Some ways to help with loss of bladder control:
- Drink at least six to seven 8-ounce glasses of water a day
- Pass up things that bother the bladder, such as caffeine, alcohol and spicy foods
- Lose weight
- Do movements to help relax your bladder muscle
Dr. Attila Barabas and
Lori McInerney, APRN, at Campbell County Medical Group
Urology provide complete urological care for men and women. Dr. Barabas is a board
certified urologist who has been in Gillette for more than nine years.
Find the CCMG Urology Clinic in the
Main Clinic on the south side of
Campbell County Memorial Hospital, 501 S. Burma Avenue in Gillette, Wyoming. You can schedule an appointment
at 307.688.3636 or learn more at
www.cchwyo.org/urology.
Blog and Infographic provided by the American Urological Association,
www.urologyhealth.org